They sound similar right? They are and they are not. In short, IBD refers to chronic inflammation of the intestines whereas IBS is considered to be a non-inflammatory condition. Albeit similar in nature, they each present with different types of symptoms as well as requiring different treatment options. Here is our low down on these two painful intestinal disorders.
IBS
During the awareness month of IBS, back in April 2016, the IFFGD reported that the incidence of IBS was estimated to be 10-15% with many people undiagnosed, unaware that their symptoms fall under the guise of IBS.
IBS symptoms include:
- Bloating
- Spasms
- Excessive gas
- Stomach pain
- Irregular and changing bowel movements
IBS is categorized into three separate subtypes including IBS-C (constipation), IBS -D (diarrhea), and IBS-M (mix of both). IBS is referred to as a functional disorder (much the same of Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue) and is considered as chronic. Albeit there is no specific test to confirm a diagnosis or specific known cause, this condition is considered very real and not just a psychological condition.
IBD
There are various types of IBD which include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and indeterminate colitis. Unlike IBS, IBD is recognized as a classified ‘disease’ which in layman’s terms means that the symptoms presented have an identifiable cause.
Colitis is an inflammation of the colon which is where the main difference from where it stands against IBS. IBD can present with very similar symptoms as IBS, which we detailed above, however, other symptoms of IBD can include:
- eye inflammation
- extreme fatigue
- intestinal scarring
- joint pain
- malnutrition
- rectal bleeding
- weight loss
What Part Does Stress Play?
We all know that stress is not good for our body. It would appear that IBS is somewhat amplified when stress is present. IBD does not seem to be caused by stress. More research is required on this front however but one thing is for sure, stress is not something that is going to help any condition. You would be doing yourself a big favour to look at ways to reduce the stress in your life.
Easy to adopt strategies include:
- Exercise regularly
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Practicing mindfulness
Natural Or Prescription Route?
IBS is often treated using antispasmodics for intestinal health but most healthcare professionals will advise strongly to pursue the natural route leaving prescribed medication as a last resort.
The treatment offered for IBD will depend upon the cause and diagnosis. Treatment will focus on treating and preventing inflammation as in the long term, inflammation can have a negative impact on the body.
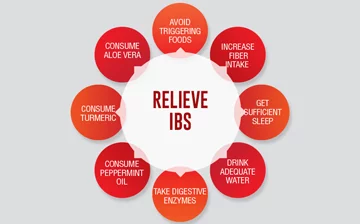
There are many natural ingredients that have been shown to help IBS including peppermint, marshmallow, ginger, aloe vera and turmeric. It is worth taking some time out to do some research and better understand what natural options you may have. If your budget will allow, a visit to a naturopath will help develop a better understanding what you can do on a purely natural level to treat your condition.
Nutritional Change
With both conditions, you may find that certain foods trigger spasms and attacks, so it will be up to you to keep a diary to track any obvious culprits. Other helpful advice includes:
- increase the fiber in your diet
- drink plenty of fluids
- eat smaller meals more frequently
- avoid foods that make symptoms worse such as alcohol, fatty foods, caffeine, spicy foods, chocolate, dairy products and artificial sweeteners
- stop smoking
- take a daily probiotic supplement
Increasing the amount of exercise you get (gentle exercise such as walking is ideal). If possible, exercising on a daily basis has been shown to help.
Do you want to find an effective IBS treatment? Check out our top rated IBS products